NIRS
Since 2022, our department has been able to measure brain processes using functional near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS or fNIRS). The German Research Foundation, the University of Mannheim and the state of BW have funded the acquisition of the device.
What is fNIRS?

fNIRS is a method for measuring blood flow changes in the peripheral regions of the brain. It is currently used in research to observe and measure cerebral functions during certain activities, such as emotional processes, learning processes or perception.
Advantages
The use of fNIRS has many advantages over other imaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). The method is non-invasive, as it does not directly interfere with tissue, and is safe and easy to use.
In addition, fNIRS measurements are virtually noiseless and can be carried out in a seated position; at the same time, there are only a few exclusion criteria. These characteristics contribute to a natural and anxiety-free setting that is suitable for all groups of people – including babies and children.
NIRS at the chair

Here at the Chair of Biological and Clinical Psychology and Psychotherapy, we use fNIRS, for example, to visualise and better understand brain processes in the processing of different stimuli in the context of anxiety disorders and post-traumatic stress disorders. In particular, we use fNIRS to investigate multisensory processes (e.g. visual & auditory stimuli), as the noiseless measurement is particularly advantageous here compared to other methods.
In some studies, for example, we use fNIRS to measure brain activity in specific brain regions during different states of consciousness. In other studies, we use this method to analyse the reactions to emotional images and sounds as well as the multisensory interactions between the different modalities. Another focus in our lab is to look at phobia-related stimuli, such as spiders, to understand how the brain reacts to fear-inducing stimuli and which neural patterns are activated.
Current studies
Current opportunities to participate in studies can be found on our homepage under ‘Studies’. You can also subscribe to our e-mail distribution list to receive regular e-mail updates on new ongoing studies at the Chair of Biological and Clinical Psychology and Psychotherapy.
Cooperation opportunities
Our research is also characterised by a large number of collaborations with various universities and institutions within Germany and internationally. You can find a list of these co-operations on our homepage under ‘Co-operations’. If you are interested in a research co-operation with us, we would be pleased if you would contact us directly.
How does NIRS work?
A NIRS device consists of two types of optodes; diodes and photodetectors. The diodes emit near-infrared light into the brain tissue. If a brain region is currently active, it requires more oxygen, which means that more blood flows through it. This means that more light is absorbed and less light is reflected. At the same time, the haemoglobin also changes its colour by releasing oxygen atoms. This in turn changes which wavelengths of light are absorbed and which are reflected.
The reflected wavelengths, whose properties have thus changed along the way, are collected again by the photodetectors and measured. This allows active regions of the brain to be visualised.
Risks and exclusion criteria

NIRS measurements are painless, have no side effects and are generally characterised by a low number of exclusion criteria. However, certain conditions can cause interference in the signal, which can make the measurement considerably more difficult. Certain hair structures, such as thick, curly or dark hair may prevent the optodes from resting properly on the scalp and therefore prevent the near-infrared light from reaching the desired areas of the brain. In such cases, test subjects might have to be excluded from measurements. In addition, it is important to record disease-related information, as certain medications and/
Technical details of the NIRS device at the chair
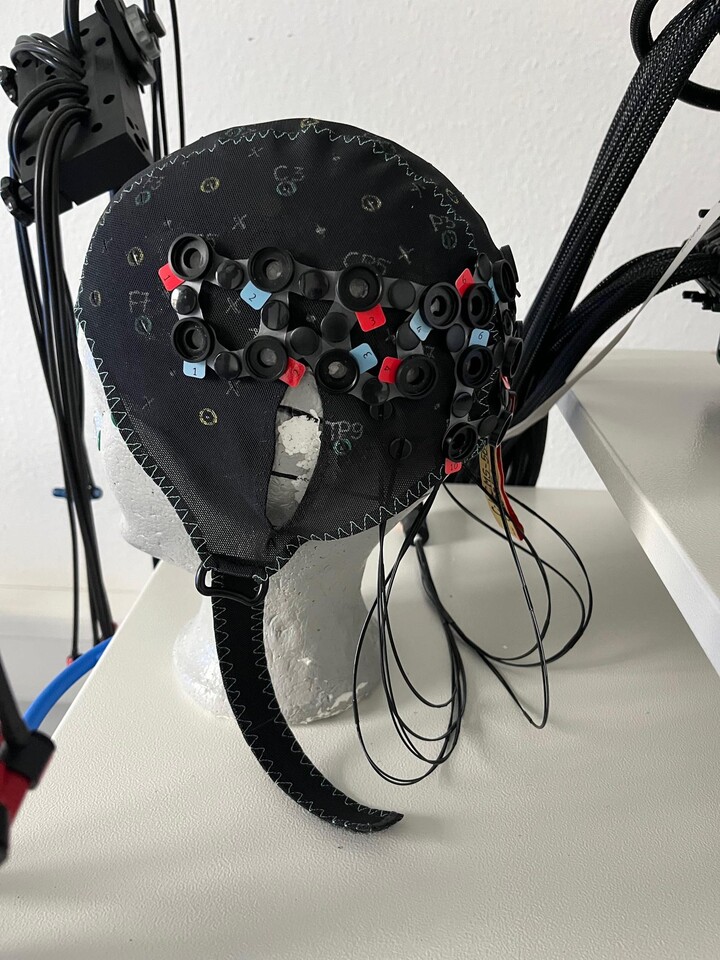
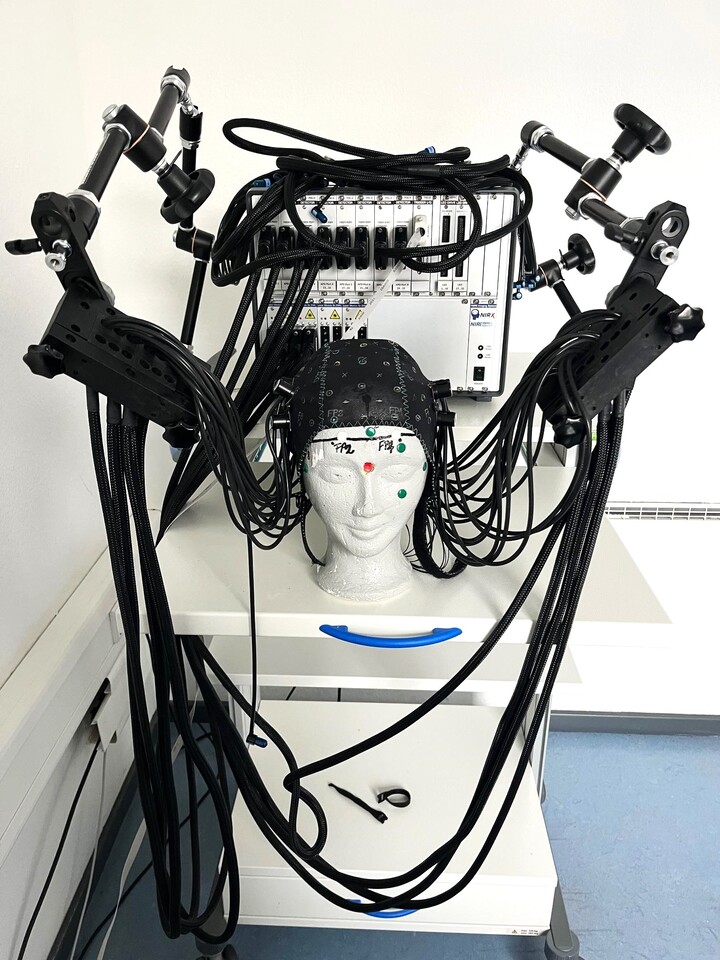
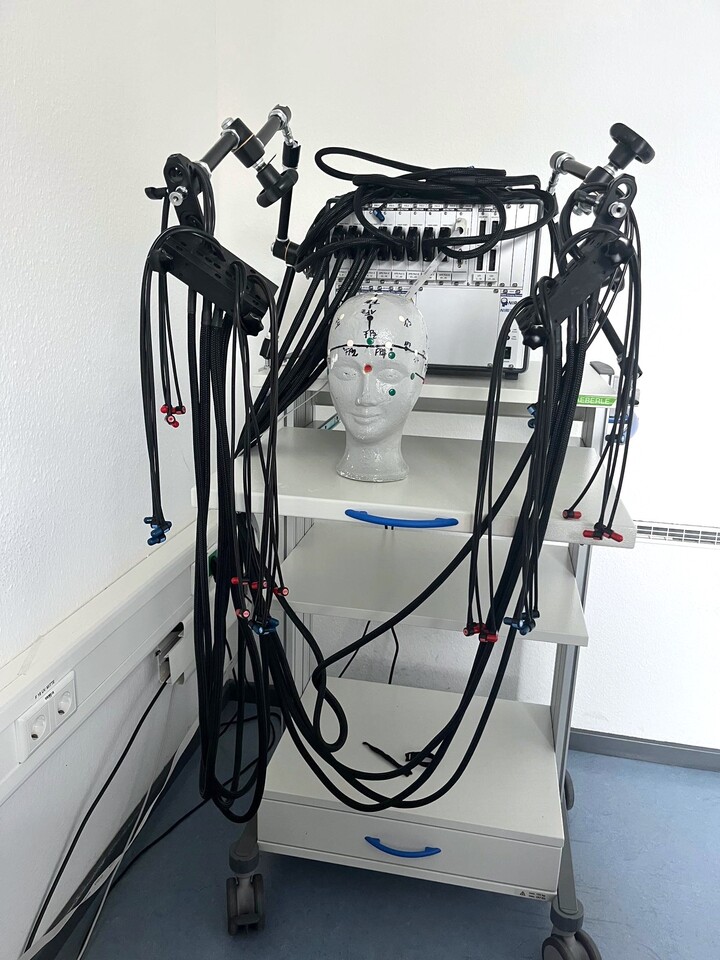
Our chair uses the NIRScout Extended Plus model from NIRx Medical Technologies, which allows us to configure the optodes in a flexible and versatile way. This system also allows the use of short channels, which means that interference signals close to the scalp can be detected and factored out in the data analysis, which significantly increases the measurement accuracy.
The NIRScout Extended Plus is ideal for multimodal measurements as it has optodes compatible with magnetic resonance imaging and transcranial magnetic stimulation and can be easily combined with electroencephalography and virtual reality. The system is also characterised by high data quality and fast installation.
In addition, the associated NIRSCap has bonnets in different sizes, which ensures optimum adaptation to different head sizes.
Publications
Publications, which were produced in cooperation with other NIRS-laboratories, can be found in the list of publications of Prof. Dr. Georg W. Alpers.